RHEOLOGY OF PARTICLE SUSPENSIONS
Fresh Concrete, Mortar and Cement Paste with Various Types of Lignosulfonates
Download:
Wallevik, J.E. (2003); Rheology of Particle Suspensions - Fresh Concrete, Mortar and Cement Paste with Various Types of Lignosulfonates (Ph.D.-thesis); Department of Structural Engineering, The Norwegian University of Science and Technology, ISBN 82-471-5566-4, ISSN 0809-103X.
https://ntnuopen.ntnu.no (search for "Jon Elvar Wallevik")
https://ntnuopen.ntnu.no/ntnu-xmlui/handle/11250/236410 (in PDF format)
Theme:
Basically, the theme of this thesis is rheology and non-Newtonian fluid mechanics of viscoplastic fluids, measurements, computational rheology and CFD.
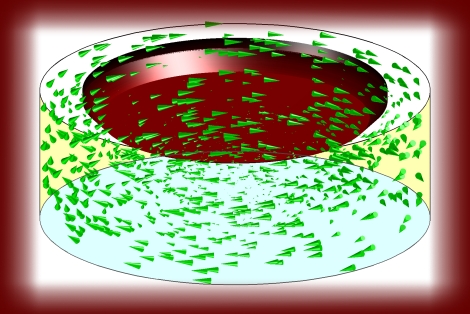
The above figure is from page 264 in my thesis (Figure 10.30). It shows the velocity profile inside a modified cone viscometer. For this figure, a Bingham fluid is applied with yield value and plastic viscosity of 200 Pa and 20 Pa.s, respectively. The top red region is the measuring unit and is stationary, while the rest of the boundary consist of a rotating bucket (here, rotating at 3 rad/s).
Full reference:
Wallevik, J. E. (2003); Rheology of Particle Suspensions - Fresh Concrete, Mortar and Cement Paste with Various Types of Lignosulfonates (Ph.D.-thesis); Department of Structural Engineering, The Norwegian University of Science and Technology, ISBN 82-471-5566-4, ISSN 0809-103X.
Erratum and Nomenclature:
Like in most/all textbooks and other written documents, typesetting error are always present. In the following download are some correction of the above mentioned textbook Rheology of Particle Suspensions: erratum.pdf. Also included are nomenclature of the major variables in the textbook.
